Telehealth helps Minnesotans prevent diabetes
The Minnesota Department of Health has worked over the last decade to help more Minnesotans connect to the National Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP).
Over 31,500 Minnesotans have enrolled in the National DPP since 2012. Telehealth and distance learning helps make it easier for people to find a class that works for them.
In 2019, Jane Ott was diagnosed with prediabetes, a serious health condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough yet to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
Jane watched friends and family struggle with type 2 diabetes, and she knew she wanted to make some healthy lifestyle changes to prevent her prediabetes from progressing.
The National Diabetes Prevention Program, a lifestyle change program supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, has been shown to help adults lower their risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 58%.

Jane and her husband Gene run a canoe outfitting service in Ely, Minnesota. Although Jane was interested in joining the National Diabetes Prevention Program to get support to eat healthier, reduce stress, and incorporate more physical activity in her day, it was proving to be difficult. The year-long course was not being offered anywhere near Ely. Each winter, Jane and her husband drove down to Florida for a few months, so joining the course in person was just not feasible.
Then Jane discovered a National DPP course that was being offered online by CentraCare in Redwood Falls, through Juniper.
“The online program was perfect for me,” Jane said. “I wouldn't have had the opportunity to participate without it.”
Telehealth makes it easier to access health resources
Before 2020, the National Diabetes Prevention Program was offered almost solely in person, but the COVID-19 pandemic pushed providers and participants to embrace distance learning as effective and desirable ways to deliver the program. More insurance companies, including Medicare and Medicaid, were covering telehealth services provided via phones, smartphones, tablets, and computers. This expansion of coverage made it so many more people had access to health resources, including the National DPP.
Jane and her classmates met online, connecting in real time to a lifestyle coach who led the classes. Jane’s coach made sure everyone stayed on track and had the support they needed to complete the program.
Even though she joined the National DPP on her computer, Jane still felt very connected with the other participants. Sharing stories and being around others who were going through the same experience was helpful.
“I started realizing that yes, I could lose some weight, especially when I really stayed on task,” Jane said. “And as time progressed and I was seeing some weight come off and feeling better, then things kind of kicked into gear a little.”
Helping more Minnesotans prevent diabetes
Jane’s situation is not unique. In Minnesota, an estimated 1.6 million adults have prediabetes. However, most people do not know they have it (about 1.2 million people).

The Minnesota Department of Health works to make sure Minnesotans have what they need to prevent or manage diabetes. MDH supports the many diabetes prevention programs across the state and the lifestyle coaches that run them by making sure they have the skills needed to deliver the program. For example, MDH State Quality Specialists connect quarterly with coaches across the state to discuss lifestyle change-related topics, share best practices, and updates on the program from the CDC. It also includes making sure programs have what they need to deliver the program via telehealth.
Over the past 13 years, MDH has helped make the National Diabetes Prevention Program more available across Minnesota.
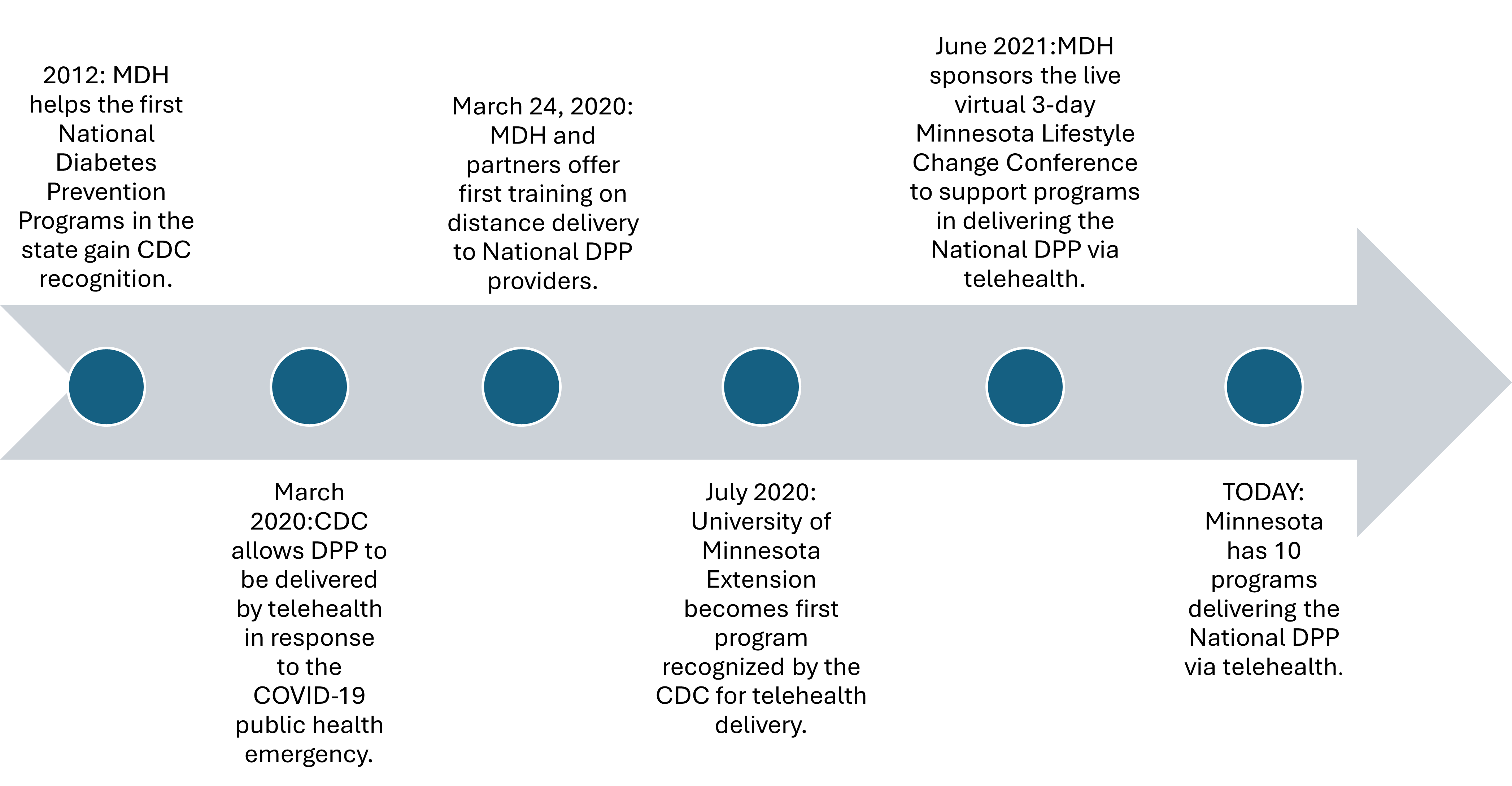
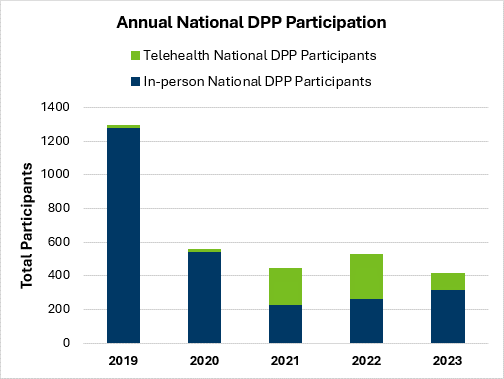
Although participation dropped significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic, participation is working back up to pre-pandemic levels with support from MDH and expanded telehealth options. For enrollment to continue to grow, it is important to have options that make the program easier to access.
Jane continues to see the value in telehealth and how it has helped her reach her health goals. “I just hope that I continue to see online options for more classes and different things too.”
The Minnesota Department of Health (MDH) receives funding from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to increase access and participation in the National Diabetes Prevention Program (National DPP) and the Diabetes Management Education and Support (DSMES) program.